What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is one of the most common diseases of our time. The incidence of the disease increased significantly, especially due to lack of movement and irregular diet. In this context, those at risk are children, young adults and middle-aged individuals. Type 1 diabetes is more common in children, while type 2 diabetes appears in adults who are overweight and usually over the age of 40.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes in our country. Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90% of diabetic patients. It occurs as a result of insensitivity of the body’s cells to the hormone insulin, which determines the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Disruption of insulin secretion and resistance to insulin action in the body are the two most important factors. Most people with this disease may not have symptoms of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed incidentally in such patients. As a result of the silent development of the disease, damage to organs and blood vessels is inevitable. It is common in individuals over the age of 40 who are overweight and have a sedentary lifestyle.
How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Type 2 diabetes can be diagnosed with detailed information from the patient and blood tests. Diagnosis of this disease. If the blood sugar is above 200 mg at any time If the blood sugar is still above 200 mg in the second hour of the glucose load, If the fasting sugar is above 120 mg Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed.
What is the treatment for type 2 diabetes?
The treatment that should be applied to a patient with type 2 diabetes varies depending on the course of the disease and how far it has spread. Usually the treatment is as follows; Depending on the diabetes, an appropriate diet and exercise program specific to the patient’s height, weight, lifestyle, and insulin drug therapy are implemented. In cases where medical treatments are insufficient for the patient, surgical treatment is applied.
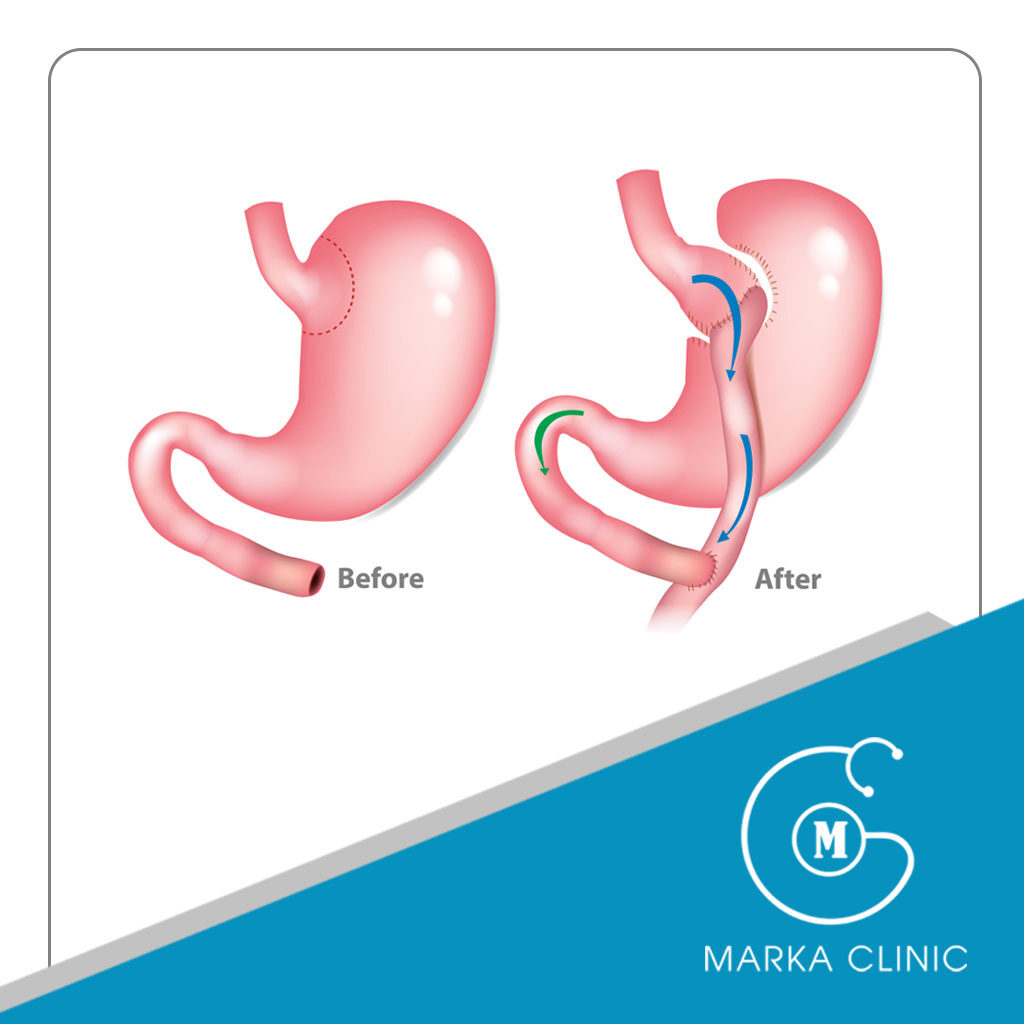
How long is the rerouting process?
Bypass surgery takes an average of two hours. The risks after gastric bypass surgery are very low, as it is performed laparoscopically without damaging the organ, protecting the gastric inlet and outlet, and ensuring continuity in the digestive system.
Who is the appropriate surgical treatment?
Surgical treatment is not appropriate for every diabetic patient. The most suitable people for surgical treatment are patients with type 2 diabetes. However, as a result of the fact that a person has had type 2 diabetes for years, the body’s insulin production may not be enough for surgical treatment. For this reason, the level of insulin in the pancreas must be measured before surgical treatment. The level of insulin is checked by a blood test. On the other hand, the weight of the patients is also very important. In this context, the patient’s BMI should also be appropriate for surgical treatment. To be suitable for surgical treatment, the BMI must be 35 and above. However, patients who do not respond to conventional medical treatment methods and who have a BMI of 30 and above may also be treated with surgery. Another criterion for the appropriateness of surgical treatment is that type 2 diabetes mellitus is not very advanced. In the malignant development of type 2 diabetes, the insulin stores are depleted, as a result of which various damages occur, such as damage to organs and blood vessels. Successful results are obtained with appropriate treatment and surgical procedures by identifying the patient before the insulin reserves run out.